Python 101: Lists and Tuples
Lists and tuples are two of the most important data structures in Python
Welcome to this tutorial on Python lists and tuples. Lists and tuples are two of the most important data structures in Python, and understanding how to use them is essential for any coding student. In this tutorial, we will cover the following topics:
What are lists and tuples in Python?
Creating lists and tuples
Accessing elements in lists and tuples
Modifying elements in lists and tuples
Common operations and methods for lists and tuples
So, let's get started!
What are lists and tuples in Python?
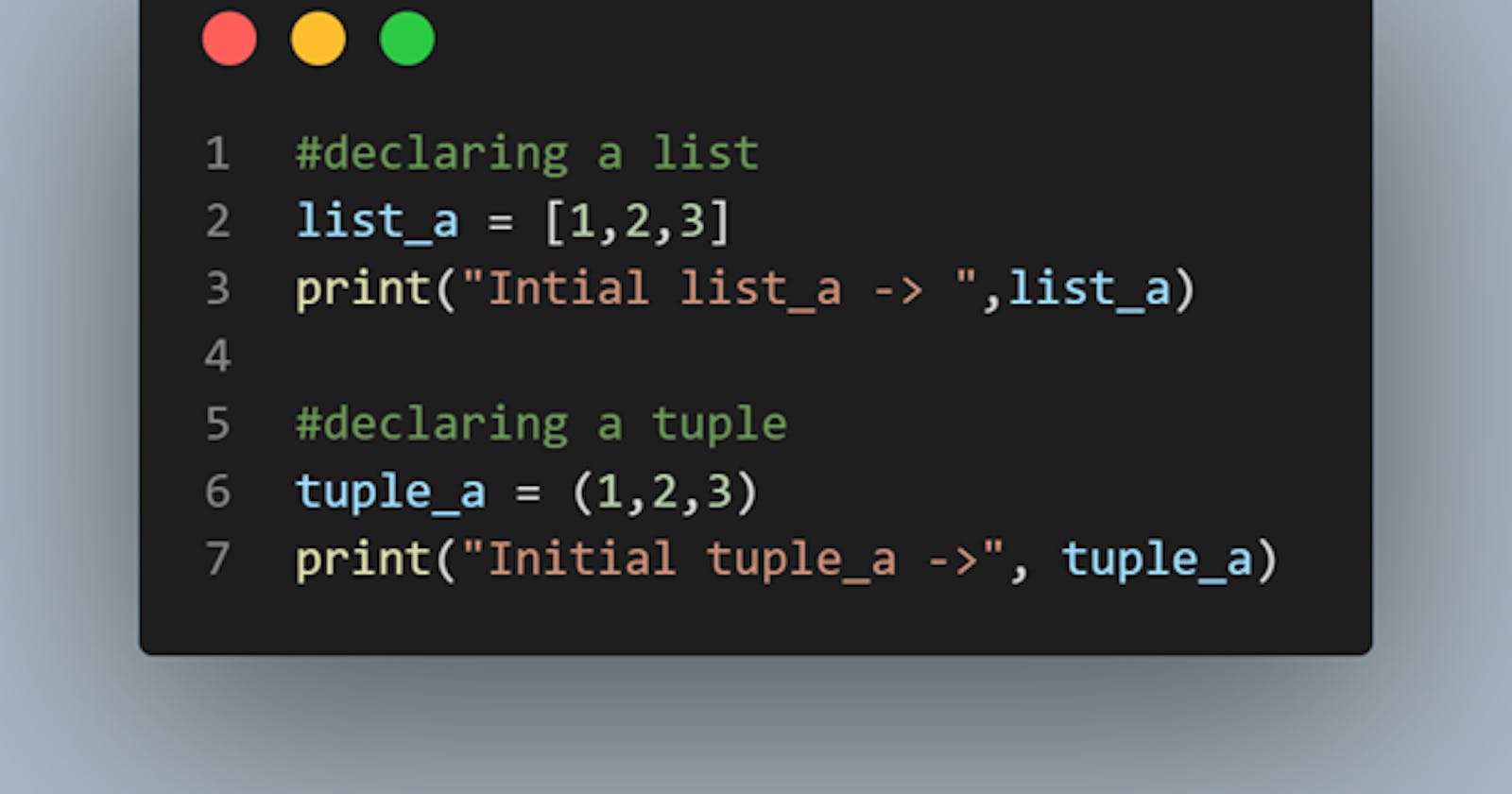
In Python, a list is a collection of items that are enclosed in square brackets [] and separated by commas. Lists can contain any type of data, including numbers, strings, and other data structures. For example, the following is a list of integers:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
A tuple, on the other hand, is similar to a list, but it is enclosed in parentheses () and the items inside are separated by commas. Tuples are also immutable, meaning that their elements cannot be changed once they are created. For example, the following is a tuple of strings:
my_tuple = ('apple', 'banana', 'orange')
Creating Lists and Tuples
Creating a list or a tuple in Python is very simple. To create a list, you simply need to enclose the items inside square brackets and separate them with commas. For example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Creating a tuple is similar, but you need to enclose the items inside parentheses and separate them with commas. For example:
my_tuple = ('apple', 'banana', 'orange')
You can also create an empty list or tuple by simply using empty brackets or parentheses:
my_empty_list = []
my_empty_tuple = ()
Accessing Elements in Lists and Tuples
Accessing elements in a list or tuple is very simple. You can access an element by its index, which is the position of the element in the list or tuple. The index of the first element is 0, the index of the second element is 1, and so on. For example, to access the first element of the list my_list, you can use the following code:
first_element = my_list[0]
You can also access elements in a tuple in the same way, but remember that tuples are immutable, so you cannot modify the elements once they are created.
Modifying Elements in Lists and Tuples
As mentioned earlier, lists are mutable, which means that you can modify the elements once they are created. You can do this by using the index of the element and assigning a new value to it. For example, to change the first element of the list my_list to 10, you can use the following code:
my_list[0] = 10
On the other hand, Tuples are immutable, which means you cannot modify the elements once they are created.
Common Operations and Methods for Lists and Tuples
Here are some common operations and methods that you can use with lists and tuples:
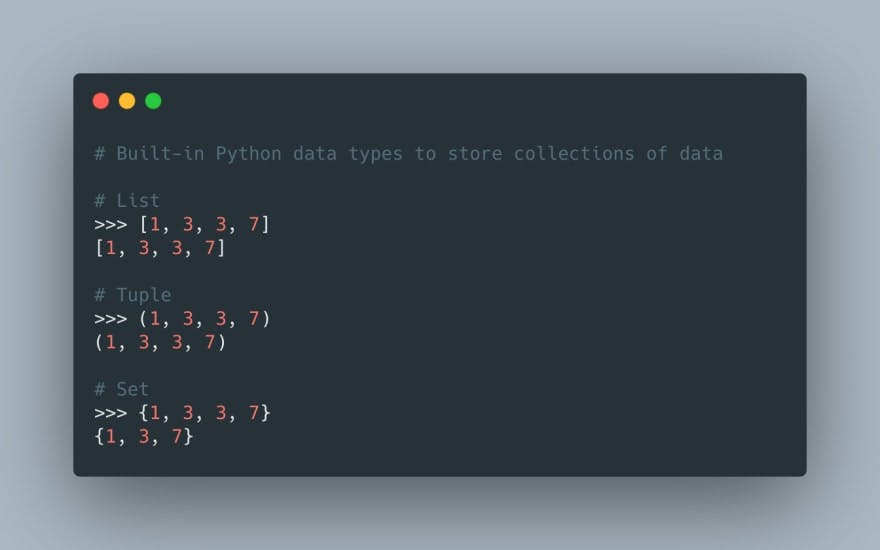
len() - This function returns the number of elements in a list or tuple.
count() - This method returns the number of occurrences of a specific element in a list or tuple.
index() - This method returns
Understanding how to create, access, and modify elements in lists and tuples, as well as common operations and methods for both, is important for any Python developer. With this knowledge, you will be able to efficiently manipulate and work with data in your programs.
I'd love to connect with you via Twitter & LinkedIn
Happy hacking!